Impressive Perfectly Elastic Momentum
Velocities After Collision For head-on elastic collisions where the target is at rest the derived relationship.
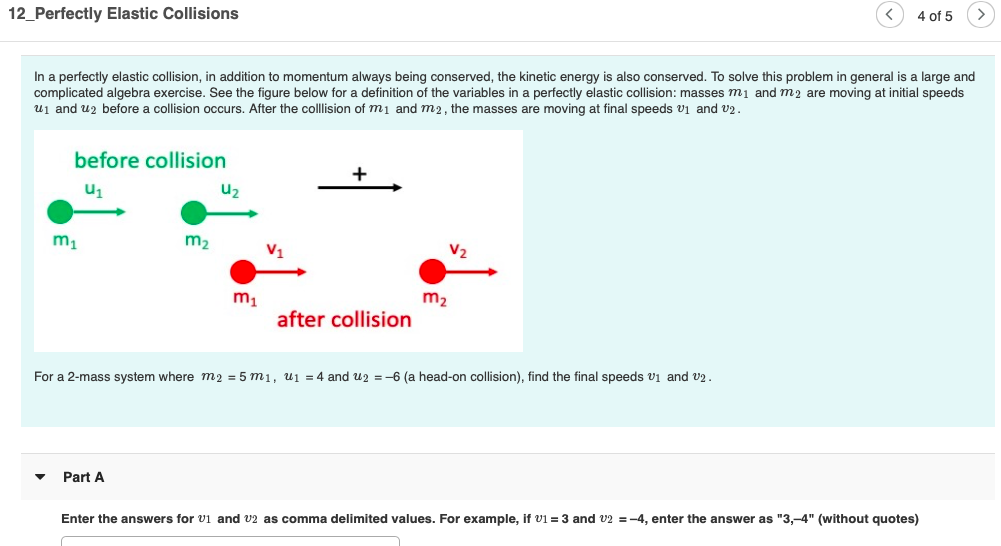
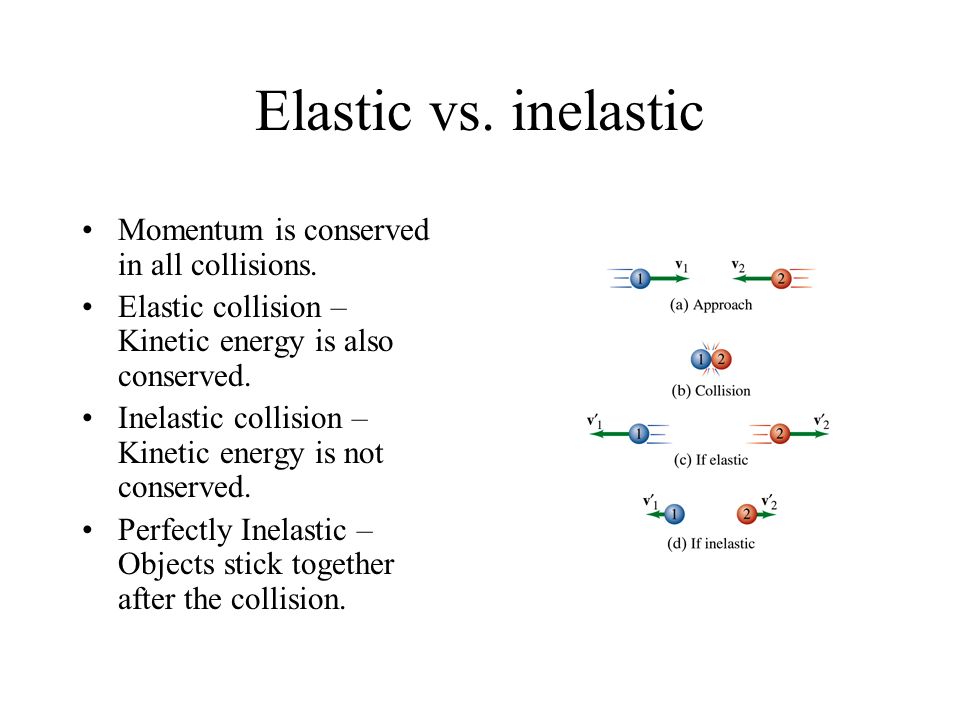
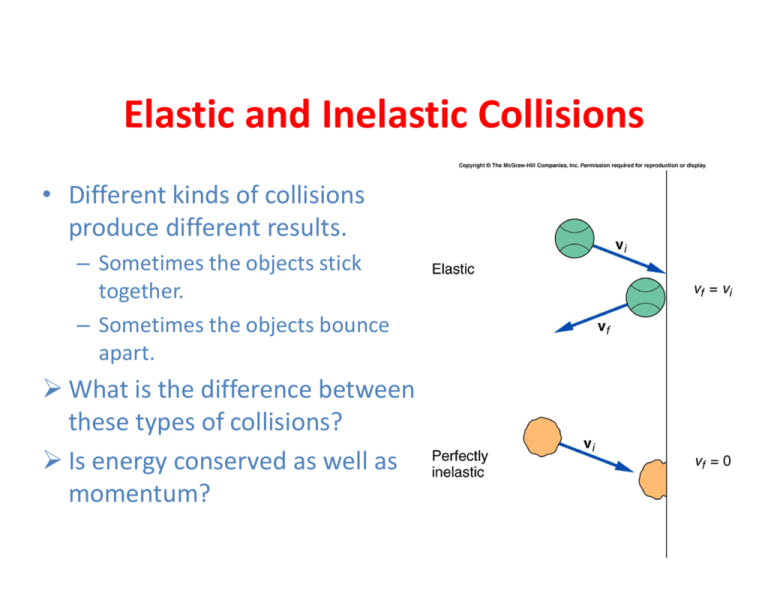
Perfectly elastic momentum. Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved quantities in elastic collisions. An inelastic collisionis one in which part of the kinetic energy is changed to. To obtain expressions for the individual velocities after the collision.
An elastic collision is a collision of 2 or more objects in which the object react perfectly elastically. Perfectly Elastic Collision Task number. Two objects collide and conserve their Kinetic Energy momentum.
In circular motion we say that speed is constant but velocity is constantly changing. P m v. A 0450-kg hockey puck moving east with a speed of 580 ms has a head-on collision with a 0900-kg puck initially at rest.
Elastic offers simple pricing without any hidden fees or prepayment penalty. In an elastic collision both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. A Find the velocity of each marble magnitude and direction after the collision.
Momentum is given by mv and kinetic energy by ½ mv2 where m is mass and v is velocity. In the physical world perfectly elastic collisions cannot truly happen. Suppose two similar trolleys are traveling toward each other with equal speed.
A Find the velocity of each marble magnitude and direction after the collision. Recall that an elastic collision is a collision in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. Their velocities are exchanged as it is an elastic collision.