Wonderful Gasoline Combustion Reaction

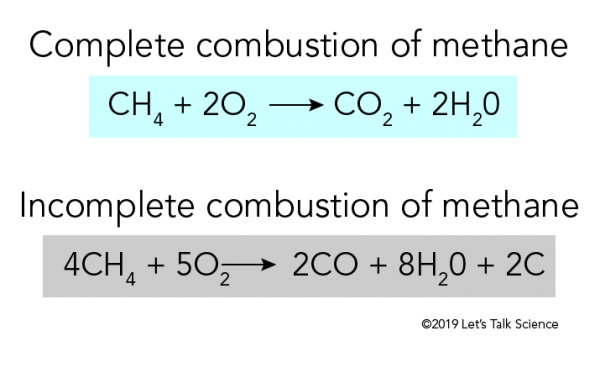
Combustion Reactions A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
Gasoline combustion reaction. It is not uncommon for combustion reactions to be accompanied by flames. Thus the reaction model of gasoline components that includes the low-temperature oxidation and ignition reaction is necessary to investigate the method to control the combustion process of the gasoline engine. A significant amount of heat energy is required to trigger such a reaction.
The combustion of hydrogen gas produces water vapor. But combustion does not occur because there is no source of heat. The combustion process also produces heat that is converted into the mechanical energy that propels the.
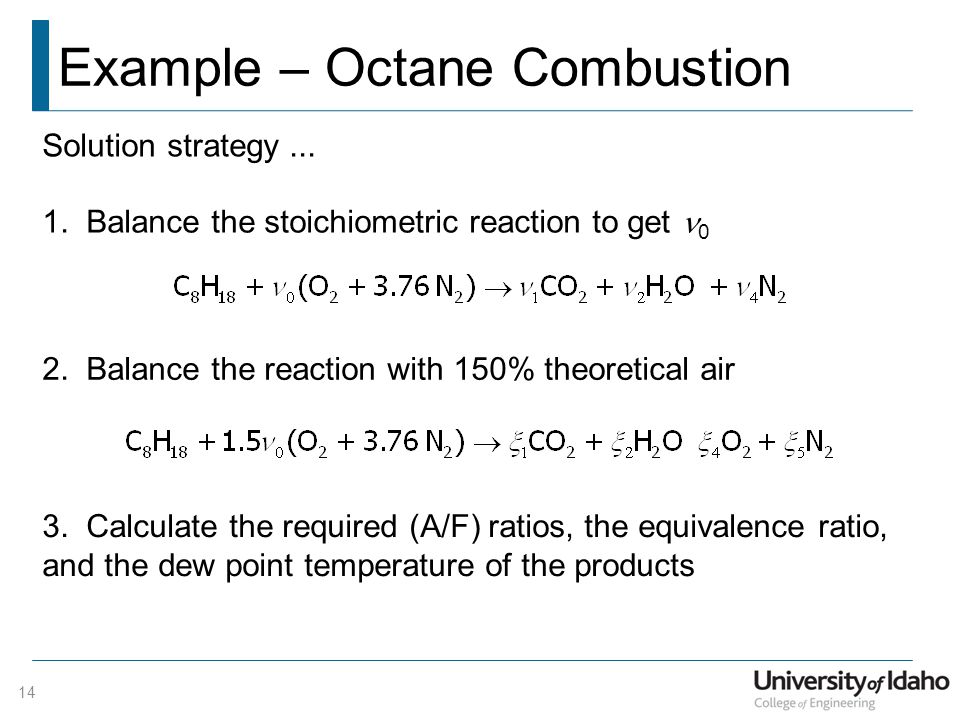
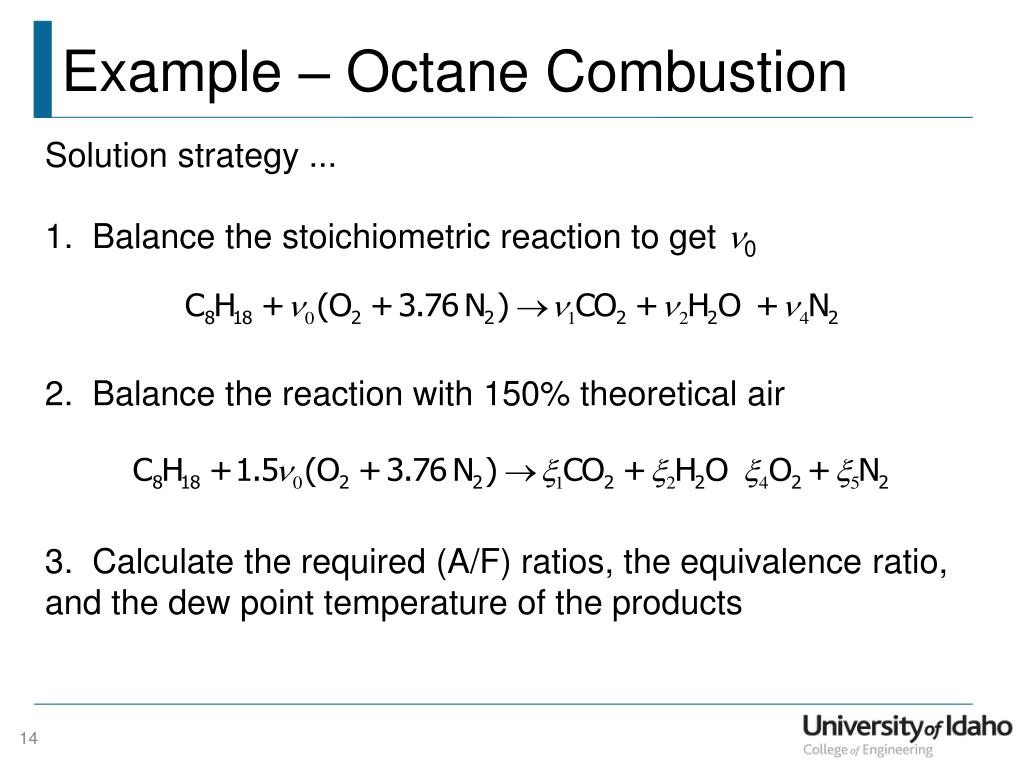
Development of Gasoline Combustion Reaction Model 2013-01-0887 Gasoline includes various kinds of chemical species. Nowadays computational fluid dynamics CFD calculations are often applied in engine design to deepen the understanding of the fuel combustion process for which accurate reaction mechanisms form the backbone While several global properties of practical fuels. Despite the increasing interest in alternative biofuels petroleum fuel remains dominant in the transport sector.
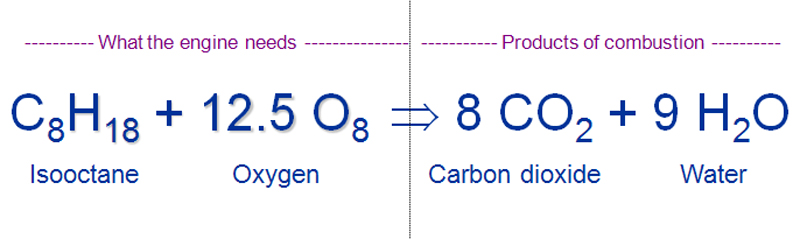
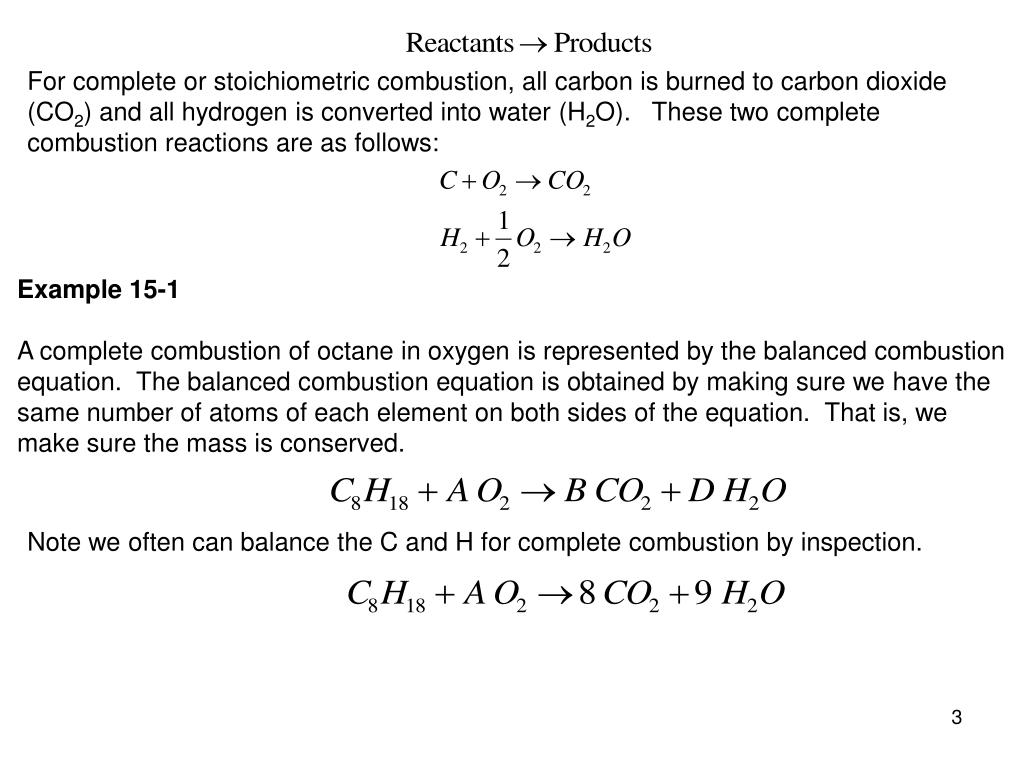
Fuel combustion also known as burning fuel is the process by which a fuel is consumed in an exothermic chemical reaction that released a great deal of heat and light. Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen and gives off heat. This is typical of combustion reactions involving hydrocarbons such as octane and propane.
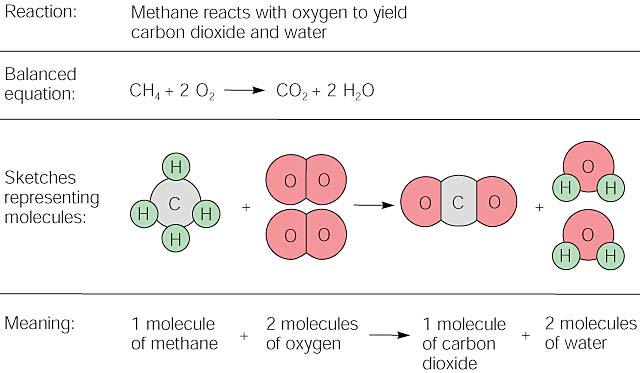
Combustion reactions must involve O 2 as one reactant. Combustion reactions are generally highly exothermic redox reactions between an oxidant and a fuel. During the combustion process as the fuel and oxidizer are turned into exhaust products heat is generated.
In a gasoline engine a mixture of gasoline and air is combusted to drive pistons. Gasoline is a refined product of crude oil and is made up of many types of hydrocarbons. Combustion or burning is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel the reductant and an oxidant usually atmospheric oxygen that produces oxidized often gaseous products in a mixture termed as smoke.