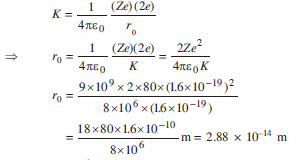Best Radius Of Closest Approach

1973 MeV fm137For example the distance of closest approach is therefore given by 1973zZ fm137T where the kinetic energyTis given in MeV.
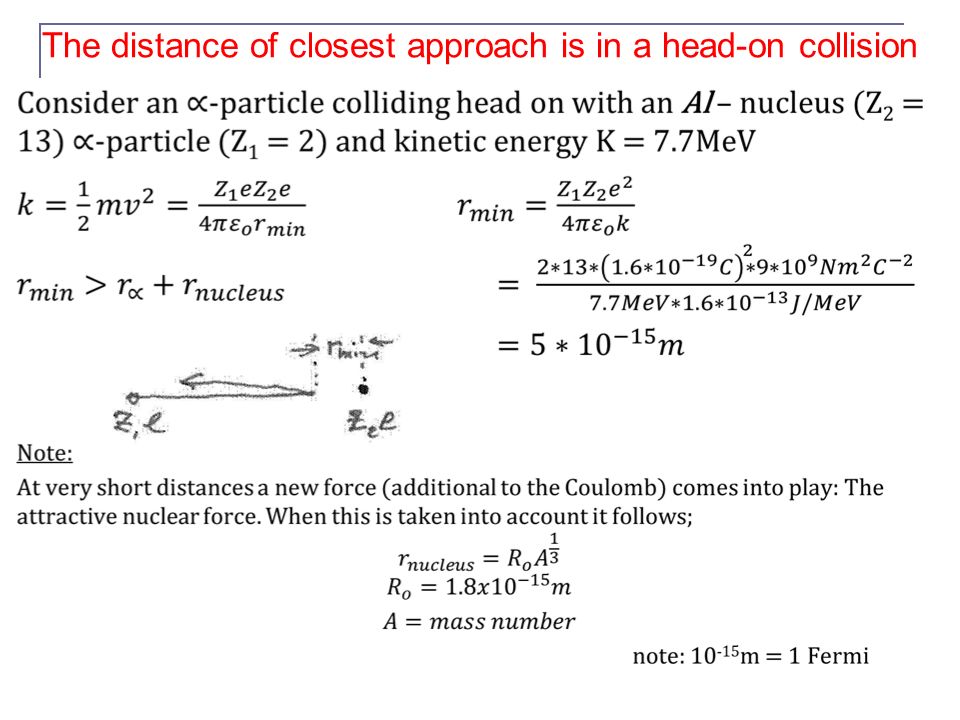
Radius of closest approach. Some of the alpha particles are detected coming straight back from the gold foil. The nucleus must be even smaller than this. A In the Rutherfords αparticle scattering experiment the distance of closest approach is 1014m.
Nuclear Radius To be able to calculate the radius of a nucleus by the closest approach of alpha particles To be able to calculate the radius of a nucleus by the diffraction angle of electrons To be able to calculate the nuclear radius and nuclear density. ThusK is doubled therefore rc becomes r2. For 5 MeV alpha particles scattered by gold nuclei this turns out to be around 5 x 10 -14 m.
35pt Consider a comet moving in a parabolic orbit in the plane of Earths orbit. Where R o is constant for all nuclei and its value is 12 x 10 -15 m. Consider a comet moving in a parabolic orbit in the plane of Earths orbit.
Rutherford scattering was the first method used to measure the size of nuclei. An apsis plural apsides ˈ æ p s ɪ d iː z AP-sih-deez from Greek orbit is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary bodyThe apsides of Earths orbit of the Sun are two. Nucleus has no definite boundary but its radius is given by following relation.
R R o A 13. If the initial kinetic energy of the alpha particles is known the distance of closest approach can be calculated. It is the distance of charged particle from the centre of the nucleus atwhich the whole of the initial kinetic energy of the far off chargedparticle gets converted into the electric potential energy of the systemDistance of closest approach rc is given byrc is inversely proportional to K.
From the closest approach calculationfor this energy and angle the impact parameter is 744 fm and the closest approach is 129 fm. The nuclear radius is the distance from the centre of the nucleus at which the density of nuclear material decreases to one-half of its maximum value at the centre. At the time of collision the two sphere centers and the point of closest approach will form a right triangle.